GCSE Probability
Course Description
Statistics & Probability makes up 12 – 18% of the Edexcel GCSE Maths Examboard.
The key concepts covered for GCSE probability include:
- Probability
- Venn diagram
- Probability from a Venn diagram
- Independent combined events
- Dependent combined events
If you have any questions please contact us. You can also book a FREE TRIAL HERE
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Background Information Below
So what is probability?
Probability is about estimating or calculating the likelihood of something happening. This could be by describing using words for example impossible, unlikely, likely, certain or could be by actual calculation where 0 means impossible and 1 means certain and a number in between if closer to 1 will indicate that it’s more likely and if its further away from 1 will indicate that it’s less likely. This could be represented on a scale as shown below:
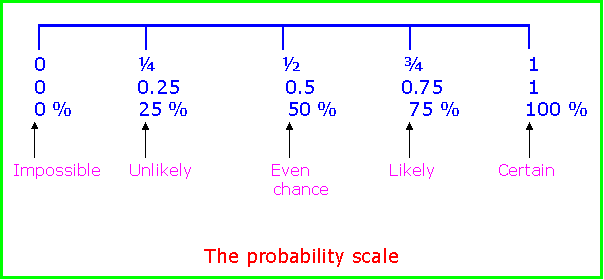
Probability could be written as a decimal, fraction or a percentage. If a probability of each event happening is written as a decimal or a fraction then the probability must always add up to 1. If it is written as a percentage then the sum of all probabilities should add up to 100%. For example, if a bag has a red and blue counter then the probability of picking out a red and blue counter from the bag is 1 (as a decimal) or 100% (as a percentage) indicating that it will definitely happen.
Exam Technique:
There are usually two types of GCSE probability questions that come up in the exam.
- Single events
- Multiple events
Single Event Example
Question: There is a bag filled with 9 red counters, 2 blue counters, 3 yellow counters and 1 green counter. What is the probability of choosing a red counter.
Answer: In this case, the probability of choosing a red counter is the number of red counters divided by the total number of counters = 9 / (9+2+3+1) = 9 / 15 = 0.6 = 60%.
Multiple Event Example
When given a wordy GCSE probability question – it’s always useful to use diagrams to help you visualise and understand the question. In GCSE Maths understanding a question is essential. For example, a question could be:
“A six fair sided dice is rolled twice, what is the probability of obtaining a number 6 the first time and not a 6 the second time the dice is rolled?” To answer this GCSE probability question, one can start off by drawing a probability tree diagram to better visualise the GCSE question as shown below.
One can then see that the probability of scoring a 6 and not a 6 is 1/6 and 5/6. Therefore, multiplying these probabilities together will give you the answer. In this case 1/6 x 5/6 = 5/36. Please note that drawing a probability tree diagram is not always required although it will contribute towards obtaining method marks.
Important: When answering a GCSE probability question, one should look at what the question is asking you. If a question is asking you to find the probability of rolling a six AND not rolling a six then you MULTIPLY these probabilities together. If the question is asking you what is the probability of rolling a six OR not a six then you ADD the probabilities together. This is an important distinction to make a note off.
Our tutors have gone through the UK curriculum themselves and have sat the GCSE & A-level examinations. Our tutors are therefore very familiar with the curriculum are best suited to help boost your grade.
London Tuition Academy has expert GCSE Maths tutors that can best support you. Please contact us TODAY if you need help with GCSE Geometry & Measures or GCSE Maths you can also book a FREE TRIAL HERE!


